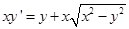 ..(ii)
..(ii)
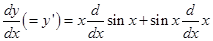 =
= 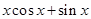
L.H.S. of eq. (ii) = 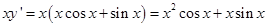
R.H.S. of eq. (ii) = 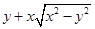 =
= 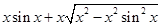 [From eq. (i)]
[From eq. (i)]
= 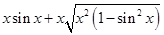 =
= 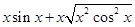
= 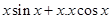 =
= 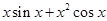
= 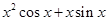
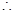 L.H.S. = R.H.S
L.H.S. = R.H.S
Hence, 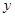 given by eq. (i) is a solution of
given by eq. (i) is a solution of 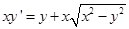 .
.
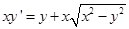 ..(ii)
..(ii)
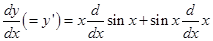 =
= 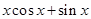
L.H.S. of eq. (ii) = 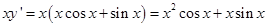
R.H.S. of eq. (ii) = 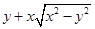 =
= 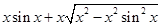 [From eq. (i)]
[From eq. (i)]
= 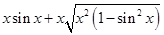 =
= 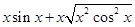
= 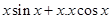 =
= 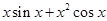
= 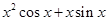
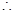 L.H.S. = R.H.S
L.H.S. = R.H.S
Hence, 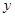 given by eq. (i) is a solution of
given by eq. (i) is a solution of 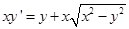 .
.