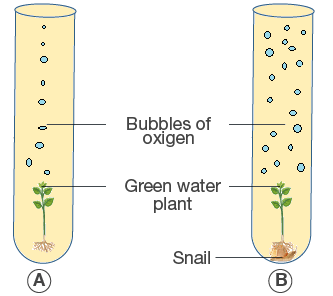
(a) Name the physiological process that releases the bubbles of oxygen.
(b) Explain the physiological process as mentioned above in (a).
(c) What is the purpose of keeping a snail in test-tube B?
(d) Why does test-tube B have more bubbles of oxygen?
(e) Give an example of a water plant that can be used in the above experiment.
(f) Write the overall chemical equation for the above process .
Solution –
- Name the physiological process that releases the bubbles of oxygen.
Answer – Photosynthesis is the physiological process that releases the bubbles of oxygen
- Explain the physiological process as mentioned above in (a).
Answer – photosynthesis is an important activity performed by all green plants by which they prepare their food . They synthesis food from carbon dioxide and water in the presence of chlorophyll and light energy.
- What is the purpose of keeping a snail in test-tube B?
Answer – it increases the rate of photosynthesis by increasing the concentration of carbon dioxide.
- Why does test-tube B have more bubbles of oxygen?
Answer – the plant in test tube B has more concentration of CO2 available because the snail releases CO2 during respiration. This increases the rate of photosynthesis in the plant placed in test tube B which leads to the release of more amount of oxygen.
- Give an example of a water plant that can be used in the above experiment.
Answer – hydrilla
- Write the overall chemical equation for the above process .

