Solution: The schematic diagram of the simple electric motor is:
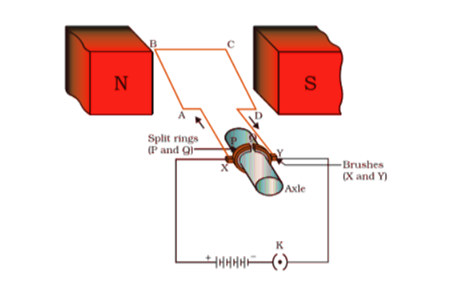
A BCD coil is a coil that is placed between the two poles of a permanent magnet to create a magnetic field. The coil is positioned in such a way that the current flows in a direction that is perpendicular to the magnetic field’s direction of rotation.
• The coil’s arms are connected to a split ring, which is divided into two halves, P and Q. Arms AB and CD are attached to the half P, and arms AB and CD are attached to the half Q, respectively. • Split rings X and Y are in contact with two static brushes (X and Y), which provide them with electricity supply. From the inside, the split rings are insulated against the elements. The split rings are being passed through by an axle. • Electric current is supplied to the coil by means of a battery. The flow of current is from point A to point B and from point C to point D.
An electric motor, as depicted in Figure, is composed of a rectangular coil ABCD of insulated copper wire wrapped around a shaft. Coil placement between two poles of a magnetic field must be done in such a way that the arms AB and CD are parallel to the direction of the magnetic field. In this case, the coil’s ends are connected to the two halves P and Q of a split ring at their ends. In addition to being insulated, the inner sides of these halves are attached to an axle. The external conducting edges of P and Q come into contact with two conducting stationary brushes, X and Y, which are in turn in contact with each other. The current in the coil ABCD is drawn from the source battery by means of the conducting brush X and returned to the battery by means of the conducting brush Y. It is important to note that the current in coil arm AB flows from A to B. It flows from C to D in arm CD, which is the polar opposite of the direction of current flowing through arm AB.
Following Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule to the letter. When current flows from point A to point B, the coil’s arm AB moves to the right. On the other hand, when current flows from C to D, the arm CD moves up one position.
When the coil has completed one-half of a turn. Brush Y is touched by P of the split ring, and the inverse is true for Q of the split ring. It follows as a result of this that the current is reversed. This indicates that current is now flowing from D to C and from B to A. CD is pushed down and AB is pushed up as a result of this. As a result, the coil continues to turn indefinitely.
Electric motor with a simple design Electric motor for commercial use.
It is necessary to use a permanent magnet.
It is necessary to use an electromagnet magnet.
The number of turns in the coil is less. The number of turns in the coil is high.
There is no use of an iron core. The core is made of soft iron.
