Ready to learn about the valency of halogens? Halogen atoms have a certain number of electrons in their outermost energy level, which determines how they react with other atoms. This blog post will explore the valencies of the five main halogens- chlorine, fluorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine. So what are you waiting for? Read on to learn more!
What is meant by the term Valency?
In chemistry, valency refers to the number of chemical bonds an element can form. This number is determined by the number of electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom. For example, carbon has four valence electrons to form four bonds.
Valency can also describe the combined power of an atom or compound. For example, water has two valences, meaning that each molecule can connect with two atoms or molecules. Valency is also used in biology to refer to the number of sites on a protein that can bind to another molecule (such as DNA).
Finally, valency in linguistics refers to the number of arguments a verb or predicate can take. For example, the English verb “read” is transitive, meaning it takes one object (the book that is being read), while the verb “sleep” is intransitive and does not take an object.
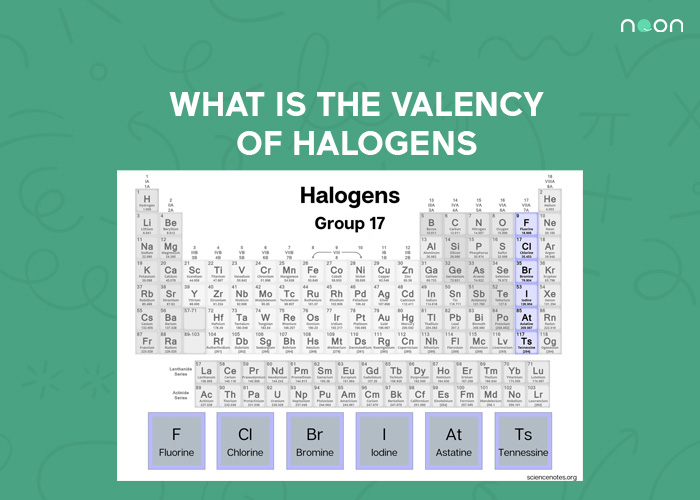
Valency of Halogens
The halogens are a group of five elements in the periodic table: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At). All of these elements have seven electrons in their outermost energy level, giving them a valence of -1. This means they are eager to lose that one electron to form a stable compound.
As a result, halogens are highly reactive and often used as disinfectants or cleaning agents. When combined with other elements, the halogens form compounds with different properties depending on the identity of the other component.
For example, fluorine is the most minor and most reactive halogen, so it forms compounds that are very strong and stable. On the other hand, iodine is the largest and least reactive halogen, so it forms compounds that tend to be weaker and less stable.
Comparison of Reactivity of Halogens
there are some important differences between the halogens. Fluorine is the most reactive of the halogens, and it is also the smallest. As a result, it forms powerful bonds with other atoms and is often used in industrial processes.
Chlorine is less reactive than fluorine but is still a powerful oxidising agent. It is also one of the most abundant halogens on Earth, making it a key ingredient in many products and substances.
Bromine is less reactive than chlorine, but it can still form strong bonds. It is primarily used as a flame retardant and in some medical applications. Iodine is the least reactive of the halogens, but it still has some important uses.
For example, it is used in radiotherapy and as a tracer element in medicine. Astatine is the most radioactive of the elements, and as a result, it has very few practical applications. However, it still plays an important role in research due to its unique properties.