What is a proton?
Protons are the positively charged particles present in the nucleus of an atom.
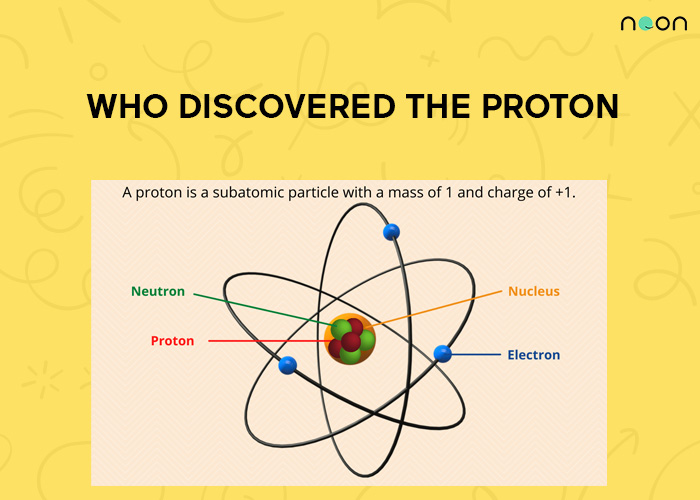
Structure of an atom
- An atom contains protons, electrons, and neutrons, with the nucleus at the center.
- The nucleus contains protons and neutrons.
- Protons and neutrons are also called nucleons.
- Electrons revolve around the nucleus in circular orbits.
- Charge can be positive or negative
- Relative charge is used to compare particles
- Electron’s charge is negative
- Proton’s charge is positive
- Neutrons have no charge.
- An atom is actually neutral in nature.
- Nuclear charge is normally stated as the relative charge of the nucleus.
- The proton number is the number of protons in a nucleus.
- Since nuclei are made up of only protons and neutrons, the proton number determines the relative charge on a nucleus.
- In any atom the number of protons and electrons is always equal.
- The entire mass of an atom is concentrated in the nucleus.
- Relative mass is a way of comparing particles. It is measured in atomic mass units (amu)
- A relative mass of a proton is equal to mass of 1.67 × 10-27 kg
- The relative mass of a nucleus only includes the protons and neutrons. However, this is pretty much the relative mass of the whole atom because electrons have negligible (very little) mass in comparison to the proton and neutron.
| Particle | Relative charge | Relative mass |
| Proton | +1 | 1 |
| Neutron | 0 | 1 |
| Electron | -1 | 1/2000 (Negligible) |
Discovery of the proton
- When was the proton discovered? E. Goldstein in the year 1886 found that the charge to mass ratio of the positive particles depends on the nature of the gas which is present in the discharge tube. This indicates that the charge to mass ratio (e/m) was different for different gasses.
- Godstein’s equipment consisted of a long cylindrical tube sealed at both ends and fitted with two metal electrodes. The electrodes are connected to a source of high voltage. The tube is connected to a vacuum pump to increase or decrease the pressure. The discharge tube is filled with hydrogen gas. A perforated cathode was used in the center of the tube.
- He passed electricity at high voltage and at low pressure through hydrogen gas taken in a discharge tube.
- A stream of heavy particles were given out by the anode (+ve electrode). This stream of particles is called anode rays. The particle in the discharge tube was named as a proton.
- Goldstein found that e/m of the positive rays was highest in case of the hydrogen gas that was used in the discharge tube. This is mainly because hydrogen has the lightest atom, e/m ratio will be highest.
- A proton can be produced when we remove an electron from the hydrogen atom.
H (hydrogen atom) → H+ (proton) + e– (electron)
So, a proton is a hydrogen ion (H+).