To put it simply, glucose and fructose are two types of important carbohydrates required by the body. They are further divided into two distinct classes of simple sugars: Monosaccharides and Disaccharides.
Let’s look at the chemical structure of glucose and fructose, their formula and how they are formed:
What is a Monosaccharide?
A monosaccharide is the most fundamental type of carbohydrate. Monosaccharides play a variety of tasks within cells. The primary function of monosaccharides is the production and storage of energy.
By digesting the monosaccharide glucose and processing the energy released from the bonds, most species can produce energy such as glucose and fructose. The sugars glucose and fructose are both examples of monosaccharides. But the chemical structure of glucose and fructose is different.
Glucose C6H12O6
A monosaccharide, glucose is also referred to as grape sugar. An aldohexose. The preferred energy source for our muscles and brain is glucose.
Glucose is the main type of energy needed by all living things. In photosynthesis, plants and algae use water, sunlight, and carbon dioxide to create glucose. It is naturally present in honey and fruits.
Preparation
- We can make glucose and fructose in equal amounts from sucrose (cane sugar) by heating it in an alcoholic solution with diluted HCl and H2SO4.
Formula For Glucose And Fructose
C12H22O11(Sucrose)+ H2O → C6H12O6 (Glucose)+ C6H12O6 (Fructose)
- Starch can be hydrolyzed to produce glucose at 393 K under pressure in boiled and diluted H2SO4.
(C6H10O4)n (Starch or cellulose) + nH2O + H+ → nC6H12O6 (Glucose)
Uses of Glucose
- It supplies calories from carbohydrates, making it suitable for people who are very unwell and unable to eat.
- It is utilized for the treatment of hypoglycemia.
- It functions as a precursor in the synthesis of matter.
Fructose C6H12O6
Fruits and vegetables naturally contain fructose, also known as fruit sugar, which our livers process predominantly. Energy is produced from fructose through the glycolytic cycle.
Contrary to glucose, fructose assists in the process of lipogenesis, which is how fat is produced. Fructose is a member of the ketose family. When fructose interacts with other monosaccharides, oligosaccharides are created.
Sucrose has a fructose molecule attached to a glucose molecule via a glycosidic link. Fructose binds to cellular proteins seven times more quickly than glucose does.
How Fructose is formed?
Due to the hemiketal’s stability and internal hydrogen bonds, crystalline fructose forms a six-membered cyclic structure called D-fructopyranose. It primarily exists in honey, vine fruits, the majority of root vegetables, berries, and flowers. Sugar cane, maize, and sugar beets can all be used to produce them commercially.
Uses of Fructose
- The flavour of food can be improved by using crystalline fructose.
- Fruit sugar produces soft, moist cookies, nutrition bars, and other low-calorie goods.
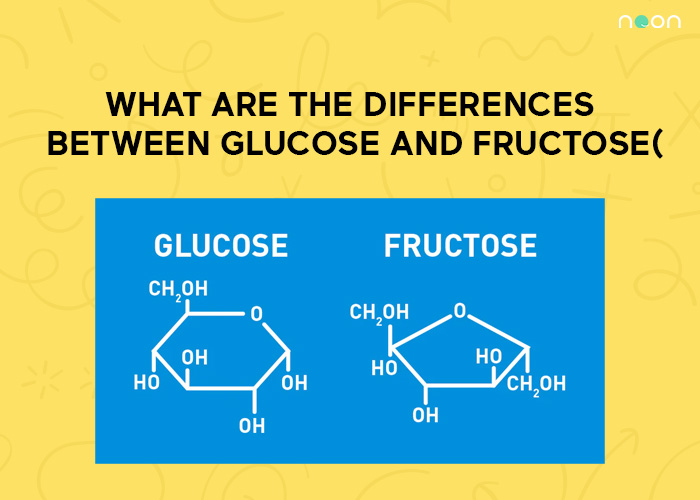
Difference Between Glucose and Fructose
| GLUCOSE | FRUCTOSE |
| Commonly known as grape sugar | Commonly known as fruit sugar |
| Six-membered ring | Five-membered ring |
| Main source of energy for the body | Main source of energy for brain and muscles |
| Less lipogenic | More lipogenic |
| Less fat producing | More fat producing |
| It is an aldohexose | It is a ketohexose |
Here we highlighted key differences between fructose and glucose including the formula for glucose and fructose, the chemical structure of glucose and fructose and how they’re formed. Visit Noon Academy’s website, where you’ll find accessible and engaging content to learn about other chemistry-related topics.
Noon Academy is Pakistan’s most popular social learning platform, with highly qualified experts from all around the country. You can also get study guides and past papers for tests in subjects like math, physics, biology, and other competitive examinations.