Difference Between Conduction And Convection
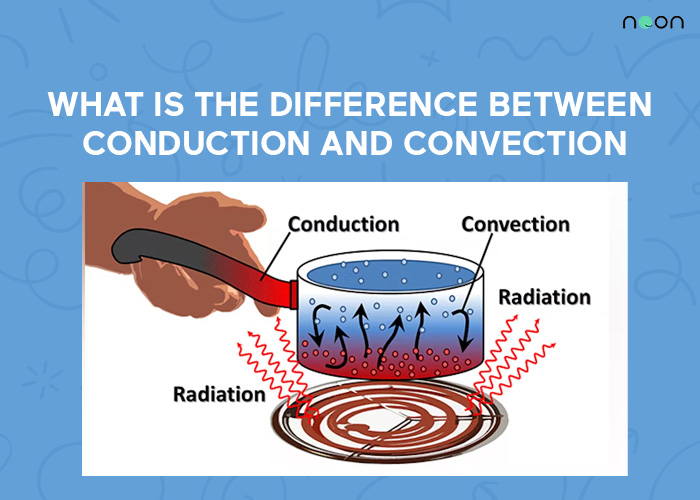
Conduction transfers heat energy from one molecule to another by direct contact. Convection is the opposite. It’s the transfer of heat energy by moving fluids (liquids or gases).
Heat always flows from a hotter object to a cooler one. When you get in touch with a hot object, you feel heat flow from the object into your hand. The hot object has more kinetic energy than the cold object. The difference in kinetic energy is converted into heat and flows from the hotter object to the colder object until both of them reach the same temperature. This flow of heat is called thermal conduction.
Thermal convection transfers heat by moving fluids (liquids or gases). Fluids are constantly in motion and this motion can be used to transfer heat. For example, when you are boiling water in a pot, the heated water near the bottom rises to the top while cooler water from the top sinks to the bottom. This movement of fluids is caused by convection.
Convection can also occur in gases. For example, when you heat air, the hot air rises while the cooler air sinks. This movement of gases is also caused by convection.
Convection Of Heat Energy
There are two main types of convection:
- Natural convection and
- Forced convection
Natural convection is the transfer of heat by moving fluids (liquids or gases) that are not mechanically forced. For example, when you are boiling water in a pot, the heated water near the bottom rises to the top while cooler water from the top sinks to the bottom. This movement of fluids is caused by natural convection.
Forced convection transfers heat by moving fluids (liquids or gases) that are mechanically forced. For example, when you use a fan to cool yourself on a hot day, the moving air causes Forced convection.
Conduction Of Heat
Some materials are good conductors of heat than others. The ability of any material to transfer heat is called its thermal conductivity. The thermal conductivity of any material is a measure of how well it conducts heat.
The units of thermal conductivity are watts per meter per degree Kelvin (W/m•K). This means that if you have a block of material that is 1 meter long, 1 meter wide, and 1 Kelvin hotter on one side than the other, the block will conduct 1 watt of heat energy from the hot side to the cold side.
The thermal conductivity of a material depends on how well its molecules can transfer heat energy. Metals are good conductors of heat because their atoms are tightly packed together, and they have free electrons that can carry heat energy from one atom to another.
Radiation
Is the transfer of heat by electromagnetic waves. All objects emit radiation. The amount of radiation emitted by any object depends on its temperature. The hotter an object is, the more radiation it emits.
You have probably experienced radiation firsthand on a hot summer day. When the sun’s rays hit your skin, you feel the heat even though there is no contact between the sun and your skin. This is because the sun’s rays transfer heat to your skin by radiation.
Thermal conductivity, convection, and radiation are ways heat can be transferred from one place to another.



