(i) (ii) Solution: (i) As the two chords \[AB\text{ }and\text{ }CD\] intersect each other at \[P\] We have \[AP\text{ }x\text{ }PB\text{ }=\text{ }CP\text{ }x\text{ }PD\] \[4.5\text{ }x\text{...
The ratio between the altitudes of two similar triangles is 3: 5; write the ratio between their: areas.
The ratio between the altitudes of two similar triangles is same as the ratio between their sides. So, The ratio between the areas of two similar triangles is same as the square of the ratio between...
The ratio between the altitudes of two similar triangles is 3: 5; write the ratio between their: (i) medians. (ii) perimeters.
The ratio between the altitudes of two similar triangles is same as the ratio between their sides. So, (i) The ratio between the medians of two similar triangles is same as the ratio between their...
Two similar triangles are equal in area. Prove that the triangles are congruent.
Let’s consider two similar triangles as \[\blacktriangle ABC\text{ }\sim\text{ }\blacktriangle PQR\] So, \[Ar\left( \blacktriangle ABC \right)/\text{ }Ar\left( \blacktriangle PQR \right)\] \[=\text{...
In the following figure, AD and CE are medians of ∆ABC. DF is drawn parallel to CE. Prove that: (i) EF = FB, (ii) AG: GD = 2: 1
Solution: (i) In \[\vartriangle BFD\text{ }and\text{ }\vartriangle BEC,\] \[\angle BFD\text{ }=\angle BEC\] [Corresponding angles] \[\angle FBD\text{ }=\angle EBC\] [Common] Hence, \[\vartriangle...
In the given triangle P, Q and R are mid-points of sides AB, BC and AC respectively. Prove that triangle QRP is similar to triangle ABC.
Solution: In \[\vartriangle ABC,\text{ }as\text{ }PR\text{ }||\text{ }BC\text{ }by\text{ }BPT\]we have \[AP/PB\text{ }=\text{ }AR/RC\] And, in \[\vartriangle PAR\text{ }and\text{ }\vartriangle...
In ΔABC, ∠ABC = ∠DAC, AB = 8 cm, AC = 4 cm and AD = 5 cm. Find the area of ΔACD: area of ΔABC
Solution: As, \[\vartriangle ACD\text{ }\sim\text{ }\vartriangle BCA\] We have, \[Ar\left( \vartriangle ACD \right)/\text{ }Ar\left( \vartriangle BCA \right)\] \[=\text{ }A{{D}^{2}}/\text{...
In ΔABC, ∠ABC = ∠DAC, AB = 8 cm, AC = 4 cm and AD = 5 cm. (i) Prove that ΔACD is similar to ΔBCA. (ii) Find BC and CD
Solution: (i) In \[\vartriangle ACD\text{ }and\text{ }\vartriangle BCA\] \[\angle DAC\text{ }=\angle ABC\] [Given] \[\angle ACD\text{ }=\angle BCA\][Common angles] Hence, \[\vartriangle ACD\text{...
In the figure given below, AB ‖ EF ‖ CD. If AB = 22.5 cm, EP = 7.5 cm, PC = 15 cm and DC = 27 cm. Calculate: (i) EF (ii) AC
Solution: (i) In \[\vartriangle PCD\text{ }and\text{ }\vartriangle PEF\] \[\angle CPD\text{ }=\angle EPF\][Vertically opposite angles] \[\angle DCE\text{ }=\angle FEP\][As DC || EF, alternate...
In the following figure, DE || AC and DC || AP. Prove that: BE/EC = BC/CP.
Solution: Given, \[DE\text{ }||\text{ }AC\] So, \[BE/EC\text{ }=\text{ }BD/DA\text{ }\left[ By\text{ }BPT \right]\] And, \[DC\text{ }||\text{ }AP\] So, \[BC/CP\text{ }=\text{ }BD/DA\text{ }\left[...
In the following diagram, lines l, m and n are parallel to each other. Two transversals p and q intersect the parallel lines at points A, B, C and P, Q, R as shown. Prove that: AB/BC = PQ/QR
Solution: Let join \[AR\]such that it intersects \[BQ\]at point \[X.\] In \[\vartriangle ACR,\text{ }BX\text{ }||\text{ }CR\] By\[BPT\], we have \[AB/BC\text{ }=\text{ }AX/XR\text{ }\ldots \text{...
In the following figure, ∠AXY = ∠AYX. If BX/AX = CY/AY, show that triangle ABC is isosceles.
Solution: According to the given question, \[\angle AXY\text{ }=~\angle AYX\] So, \[AX\text{ }=\text{ }AY\][Sides opposite to equal angles are equal.] Also, from BPT we have \[BX/AX\text{ }=\text{...
Triangle ABC is similar to triangle PQR. If bisector of angle BAC meets BC at point D and bisector of angle QPR meets QR at point M, prove that: AB/PQ = AD/PM
Solution: According to the given question, \[\vartriangle ABC\text{ }\sim\text{ }\vartriangle PQR\] And, \[AD\text{ }and\text{ }PM\]are the angle bisectors. So, \[\angle BAD\text{ }=\angle QPM\]...
Triangle ABC is similar to triangle PQR. If AD and PM are altitudes of the two triangles, prove that: AB/PQ = AD/PM.
Solution: According to the given question, \[\vartriangle ABC\text{ }\sim\text{ }\vartriangle PQR\] So, \[\angle ABC\text{ }=\angle PQR\] i.e. \[\angle ABD\text{ }=\angle PQM\] Also, \[\angle...
Triangle ABC is similar to triangle PQR. If AD and PM are corresponding medians of the two triangles, prove that: AB/PQ = AD/PM.
Solution: According to the given question, \[\vartriangle ABC\text{ }\sim\text{ }\vartriangle PQR\] \[AD\text{ }and\text{ }PM\]are the medians, so \[BD\text{ }=\text{ }DC\text{ }and\text{ }QM\text{...
In the following figure, AB, CD and EF are perpendicular to the straight line BDF. If AB = x and; CD = z unit and EF = y unit, prove that: 1/x + 1/y = 1/z
Solution: In \[\Delta \text{ }FDC\text{ }and\text{ }\Delta \text{ }FBA,\] \[\angle FDC\text{ }=\angle FBA\text{ }\left[ As\text{ }DC\text{ }||\text{ }AB \right]\] \[\angle DFC\text{ }=\angle BFA\]...
In the following figure, ABCD to a trapezium with AB ‖ DC. If AB = 9 cm, DC = 18 cm, CF= 13.5 cm, AP = 6 cm and BE = 15 cm, Calculate: PE
Solution: We already have, \[\vartriangle AEB\text{ }\sim\text{ }\vartriangle FEC\] So, \[AE/FE\text{ }=\text{ }BE/CE\] \[=\text{ }AB/FC\] \[AE/FE\text{ }=\text{ }9/13.5\] Or, \[\left( AF\text{...
In the following figure, ABCD to a trapezium with AB ‖ DC. If AB = 9 cm, DC = 18 cm, CF= 13.5 cm, AP = 6 cm and BE = 15 cm, Calculate: (i) EC (ii) AF
Solution: (i) In \[\Delta \text{ }AEB\text{ }and\text{ }\Delta \text{ }FEC,\] \[\angle AEB\text{ }=\angle FEC\] [Vertically opposite angles] \[\angle BAE\text{ }=\angle CFE\] [Since, AB||DC] Hence,...
In the following figure, XY is parallel to BC, AX = 9 cm, XB = 4.5 cm and BC = 18 cm. Find: XY
Solution: According to the given question, \[XY\text{ }||\text{ }BC\] So, In \[\Delta \text{ }AXY\text{ }and\text{ }\Delta \text{ }ABC\] \[\angle AXY\text{ }=\angle ABC\] [Corresponding angles]...
In the following figure, XY is parallel to BC, AX = 9 cm, XB = 4.5 cm and BC = 18 cm. Find: (i) AY/YC (ii) YC/AC
Solution: According to the given question, \[XY\text{ }||\text{ }BC\] So, In \[\Delta \text{ }AXY\text{ }and\text{ }\Delta \text{ }ABC\] \[\angle AXY\text{ }=\angle ABC\][Corresponding angles]...
A triangle ABC is enlarged, about the point 0 as centre of enlargement, and the scale factor is 3. Find: (i) OA, if OA’ = 6 cm (ii) OC’, if OC = 21 cm Also, state the value of: (a) OB’/OB (b) C’A’/CA
(i)\[OA\text{ }=\text{ }6\text{ }cm\] So, \[OA\text{ }\left( 3 \right)\text{ }=\text{ }OA\] \[OA\text{ }\left( 3 \right)\text{ }=\text{ }6\] Or, \[OA\text{ }=\text{ }2\text{ }cm\] (ii) \[OC\text{...
A triangle ABC is enlarged, about the point 0 as centre of enlargement, and the scale factor is 3. Find: (i) A’B’, if AB = 4 cm. (ii) BC, if B’C’ = 15 cm.
According to the given question, \[\Delta \text{ }ABC\]is enlarged and the scale factor \[m\text{ }=\text{ }3\]to the \[\Delta \text{ }ABC\] (i) \[AB\text{ }=\text{ }4\text{ }cm\] So, \[AB\left( 3...
A triangle LMN has been reduced by scale factor 0.8 to the triangle L’ M’ N’. Calculate: (i) the length of M’ N’, if MN = 8 cm. (ii) the length of LM, if L’ M’ = 5.4 cm.
According to the given question, \[\Delta \text{ }LMN\] has been reduced by a scale factor \[m\text{ }=\text{ }0.8\text{ }to\text{ }\Delta \text{ }LMN\] (i) \[MN\text{ }=\text{ }8\text{ }cm\] So,...
A triangle ABC has been enlarged by scale factor m = 2.5 to the triangle A’ B’ C’ Calculate: (i) the length of AB, if A’ B’ = 6 cm. (ii) the length of C’ A’ if CA = 4 cm.
Given that, \[\Delta \text{ }ABC\]has been enlarged by scale factor \[m\text{ }of\text{ }2.5\text{ }to\text{ }\Delta \text{ }ABC\] (i) \[AB\text{ }=\text{ }6\text{ }cm\] So, \[AB\left( 2.5...
In the given triangle PQR, LM is parallel to QR and PM: MR = 3: 4. Calculate the value of ratio: Area of Δ LQM/ Area of Δ LQN
Solution: Because, \[\Delta \text{ }LQM\text{ }and\text{ }\Delta \text{ }LQN\] have common vertex at \[L\]and their bases \[QM\text{ }and\text{ }QN\] are along the same straight line. \[Area\text{...
In the given triangle PQR, LM is parallel to QR and PM: MR = 3: 4. Calculate the value of ratio: (i) PL/PQ and then LM/QR (ii) Area of Δ LMN/ Area of Δ MNR
Solution: (i) In \[\Delta \text{ }PLM\text{ }and\text{ }\Delta \text{ }PQR\] As LM || QR, corresponding angles are equal. \[\angle PLM\text{ }=\angle PQR\] \[\angle PML\text{ }=\angle PRQ\] So,...
ABC is a triangle. PQ is a line segment intersecting AB in P and AC in Q such that PQ || BC and divides triangle ABC into two parts equal in area. Find the value of ratio BP: AB.
It’s given that, \[Ar\left( \Delta \text{ }APQ \right)\]\[=\text{ }{\scriptscriptstyle 1\!/\!{ }_2}\text{ }Ar\left( \Delta \text{ }ABC \right)\] \[Ar\left( \Delta \text{ }APQ \right)/\text{...
In the given figure, AX: XB = 3: 5. Find: (i) the length of BC, if the length of XY is 18 cm. (ii) the ratio between the areas of trapezium XBCY and triangle ABC.
Solution: According to the given question, \[AX/XB\text{ }=\text{ }3/5\] \[\Rightarrow AX/AB\text{ }=\text{ }3/8\text{ }\ldots .\text{ }\left( 1 \right)\] (i) In \[\Delta \text{ }AXY\text{...
The perimeters of two similar triangles are 30 cm and 24 cm. If one side of the first triangle is 12 cm, determine the corresponding side of the second triangle.
Suppose, \[\vartriangle ABC\text{ }\sim\text{ }\vartriangle DEF\] So, \[AB/DE\text{ }=\text{ }BC/EF\] \[=\text{ }AC/DF\] Or, \[=\text{ }\left( AB+BC+AC \right)/\left( DE+EF+DF \right)\] \[=\text{...
A line PQ is drawn parallel to the base BC of Δ ABC which meets sides AB and AC at points P and Q respectively. If AP = 1/3 PB; find the value of: (i) Area of Δ ABC/ Area of Δ APQ (ii) Area of Δ APQ/ Area of Trapezium PBCQ
According to the given question, \[AP\text{ }=\text{ }\left( 1/3 \right)\text{ }PB\] So, \[AP/PB\text{ }=\text{ }1/3\] In \[\vartriangle \text{ }APQ\text{ }and\text{ }\vartriangle ABC\] As\[PQ\text{...
1. (i) The ratio between the corresponding sides of two similar triangles is 2: 5. Find the ratio between the areas of these triangles. (ii) Areas of two similar triangles are 98 sq. cm and 128 sq. cm. Find the ratio between the lengths of their corresponding sides.
As per the given question, The ratio of the areas of two similar triangle are equal to the ratio of squares of their corresponding sides. Thus, (i) The ration is, (ii) The ratio is,
In the given figure, Δ ABC ~ Δ ADE. If AE: EC = 4: 7 and DE = 6.6 cm, find BC. If ‘x’ be the length of the perpendicular from A to DE, find the length of perpendicular from A to BC in terms of ‘x’.
Solution: According to the given question, \[\Delta \text{ }ABC\text{ }\sim\text{ }\Delta \text{ }ADE\] So, we have \[AE/AC\text{ }=\text{ }DE/BC\] \[4/11\text{ }=\text{ }6.6/BC\] Or, \[BC=\left(...
In Δ ABC, D and E are the points on sides AB and AC respectively. Find whether DE ‖ BC, if (i) AB = 9cm, AD = 4cm, AE = 6cm and EC = 7.5cm. (ii) AB = 6.3 cm, EC = 11.0 cm, AD =0.8 cm and EA = 1.6 cm.
(i) In \[\vartriangle \text{ }ADE\text{ }and\text{ }\vartriangle \text{ }ABC\] \[AE/EC\text{ }=\text{ }6/7.5\text{ }=\text{ }4/5\] \[AD/BD\text{ }=\text{ }4/5\] \[\left[ BD\text{ }=\text{ }AB\text{...
A line PQ is drawn parallel to the side BC of Δ ABC which cuts side AB at P and side AC at Q. If AB = 9.0 cm, CA = 6.0 cm and AQ = 4.2 cm, find the length of AP.
In \[\vartriangle \text{ }APQ\text{ }and\vartriangle \text{ }ABC\] \[\angle APQ\text{ }=\angle ABC\] [As PQ || BC, corresponding angles are equal.] \[\angle PAQ\text{ }=\angle BAC\] [Common angle]...
In the given figure, PQ ‖ AB; CQ = 4.8 cm QB = 3.6 cm and AB = 6.3 cm. If AP = x, then the value of AC in terms of x.
Solution: As, \[\vartriangle CPQ\text{ }\sim\text{ }\vartriangle CAB\text{ }by\text{ }AA\] criterion for similarity We have, \[CP/AC\text{ }=\text{ }CQ/CB\] \[CP/AC\text{ }=\text{ }4.8/8.4\text{...
In the given figure, PQ ‖ AB; CQ = 4.8 cm QB = 3.6 cm and AB = 6.3 cm. Find: (i) CP/PA (ii) PQ
Solution: (i) In \[\vartriangle CPQ\text{ }and\text{ }\vartriangle CAB\] \[\angle PCQ\text{ }=\angle APQ\] [As PQ || AB, corresponding angles are equal.] \[\angle C\text{ }=\angle C\] [Common angle]...
In the following figure, point D divides AB in the ratio 3: 5. If BC = 4.8 cm, find the length of DE.
Solution: Because, \[\vartriangle ADE\text{ }\sim\text{ }\vartriangle ABC\text{ }by\text{ }AA\] criterion for similarity So, we have \[AD/AB\text{ }=\text{ }DE/BC\] \[3/8\text{ }=\text{ }DE/4.8\]...
In the following figure, point D divides AB in the ratio 3: 5. Find: (i) AE/AC Also if, (ii) DE = 2.4 cm, find the length of BC.
Solution: (i) In \[\vartriangle ABC,\text{ }as\text{ }DE\text{ }||\text{ }BC\] Using BPT, \[AD/DB\text{ }=\text{ }AE/\text{ }EC\] So, \[AD/AB\text{ }=\text{ }AE/AC\] Now, \[AD/AB\text{ }=\text{...
In the following figure, point D divides AB in the ratio 3: 5. Find: (i) AE/EC (ii) AD/AB
Solution: (i) According to the given question, \[AD/DB\text{ }=\text{ }3/5\] And \[DE\text{ }||\text{ }BC\] Using Basic Proportionality theorem, \[AD/DB\text{ }=\text{ }AE/EC\] \[AE/EC\text{...
Describe: (i) The locus of the mid-points of all chords parallel to a given chord of a circle. (ii) The locus of points within a circle that are equidistant from the end points of a given chord.
i) The locus of the mid-points of the chords which are parallel to a given chords is the diameter perpendicular to the given chords. ii) The locus of the points within a circle which are equidistant...
Describe: (i)The locus of the centre of a given circle which rolls around the outside of a second circle and is always touching it. (ii) The locus of the centres of all circles that are tangent to both the arms of a given angle.
i) The locus is the circumference of the circle concentric with the second circle whose radius is equal to the sum of the radii of the given two circles. ii) The locus of the centre of all circles...
Describe: (i) The locus of points at distances less than or equal to 2.5 cm from a given point. (ii) The locus of points at distances greater than or equal to 35 mm from a given point.
i) The locus of points is the space inside and the circumference of the circle with a radius of \[2.5\text{ }cm\]and the centre as the given fixed point. ii) The locus is the space outside and...
Describe: i) The locus of points at distances less than 3 cm from a given point. ii) The locus of points at distances greater than 4 cm from a given point.
i) The locus of the points will be the space inside of the circle whose radius is \[3\text{ }cm\]and centre as the given point. ii) The locus of the points will be the space outside of the circle...
The speed of sound is 332 meters per second. A gun is fired. Describe the locus of all the people on the Earth’s surface, who hear the sound exactly one second later.
The locus of all the people on Earth’s surface is the circumference of a circle whose radius is \[332\text{ }m\]and centre is the point where the gun is fired.
Describe the locus for the locus of a point in rhombus ABCD, so that it is equidistant from i) AB and BC; ii) B and D.
(i) The locus of the point in a rhombus \[ABCD\]which is equidistant from \[AB\text{ }and\text{ }BC\] will be the diagonal \[BD\]of the rhombus. (ii) The locus of the point in a rhombus...
Describe the locus for the locus of a point P, so that: AB^2 = AP^2 + BP^2, where A and B are two fixed points.
The locus of the point \[P\]is the circumference of a circle with \[AB\] as diameter and satisfies the condition \[A{{B}^{2}}~=\text{ }A{{P}^{2~}}+\text{ }B{{P}^{2}}\]
Describe the locus for the locus of a point in space which is always at a distance of 4 cm from a fixed point.
The locus of a point in space is the surface of the sphere whose centre is the fixed point and radius equal to \[4\text{ }cm.\]
Describe the locus for the locus of vertices of all isosceles triangles having a common base.
The locus of vertices of all isosceles triangles having a common base will be the perpendicular bisector of the common base of the triangles.
Describe the locus for the locus of the centres of all circles passing through two fixed points.
The locus of the centres of all the circles passing through two fixed points will be the perpendicular bisector of the line segment joining the two given fixed points.
The locus of a points inside a circle and equidistant from two fixed points on the circumference of the circle.
The locus of the points inside the circle which are equidistant from the fixed points on the circumference of a circle will be a diameter which is the perpendicular bisector of the line joining the...
Describe the locus for The locus of the door-handle, as the door opens.
The locus of the door handle will be the circumference of a circle with centre at the axis of rotation of the door and the radius equal to distance between the door handle and the axis of rotation...
The locus of a runner, running around a circular track and always keeping a distance of 1.5 m from the inner edge.
The locus of the runner, running around a circular track and always keeping a distance of \[1.5\text{ }m\] from the inner edge will be the circumference of a circle where the radius is equal to the...
The locus of a stone dropped from the top of a tower.
Solution: As per the given question, Locus of stone is dropped from the top of tower will be vertical line through the point from which the stone is dropped.
The locus of the moving end of the minute hand of a clock.
The locus of the moving end of the minute hand of the clock will be a circle whose radius will be the length of the minute hand.
The locus of the centre of a wheel of a bicycle going straight along a level road.
The locus of the centre of wheel, is going straight along the level road will be a straight line parallel to the road at a distance equal to the radius of the wheel.
The locus of a points at a distance of 2 cm from a fixed line.
The locus of points which are at a distance of \[2\text{ }cm\]from a fixed line \[AB\]are a pair of straight lines \[l\text{ }and\text{ }m\]which are parallel to the given line at a distance of...
The locus of a point at a distance of 3 cm from a fixed point.
The locus of a point is at a distance of \[3\text{ }cm\]from a fixed point is circumference of a circle whose radius is \[3\text{ }cm\]and the fixed point is the centre of the circle.
In the given figure, AB is a side of a regular six-sided polygon and AC is a side of a regular eight-sided polygon inscribed in the circle with centre O. calculate the sizes of: ∠ABC.
Solution: According to the given question, \[AC\] is the side of a regular octagon, \[\angle AOC\text{ }=\text{ }{{360}^{o}}/\text{ }8\text{ }=\text{ }{{45}^{o}}\] Hence, \[arc\text{ }AC\]subtends...
In the given figure, AB is a side of a regular six-sided polygon and AC is a side of a regular eight-sided polygon inscribed in the circle with centre O. calculate the sizes of: (i) ∠AOB, (ii) ∠ACB,
Solution: (i) \[Arc\text{ }AB\] subtends\[\angle AOB\]at the centre and \[\angle ACB\]at the remaining part of the circle. \[\angle ACB\text{ }=\text{ }{\scriptscriptstyle 1\!/\!{ }_2}\angle AOB\]...
The given figure show a circle with centre O. Also, PQ = QR = RS and ∠PTS = 75°. Calculate: ∠PQR.
Join \[OP,\text{ }OQ,\text{ }OR\text{ }and\text{ }OS\] Given, \[PQ\text{ }=\text{ }QR\text{ }=\text{ }RS\] So, \[\angle POQ\text{ }=\angle QOR\text{ }=\angle ROS\] [Equal chords subtends equal...
The given figure show a circle with centre O. Also, PQ = QR = RS and ∠PTS = 75°. Calculate: (i) ∠POS, (ii) ∠QOR,
Solution: Join \[OP,\text{ }OQ,\text{ }OR\text{ }and\text{ }OS\] Given, \[PQ\text{ }=\text{ }QR\text{ }=\text{ }RS\] So, \[\angle POQ\text{ }=\angle QOR\text{ }=\angle ROS\] [Equal chords subtends...
If two sides of a cycli-quadrilateral are parallel; prove that: (i) its other two sides are equal. (ii) its diagonals are equal.
Let ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral in which\[AB\text{ }||\text{ }DC\] \[AC\text{ }and\text{ }BD\]are its diagonals. Required to prove: \[\left( i \right)\text{ }AD\text{ }=\text{ }BC\] \[\left( ii...
In the following figure, AD is the diameter of the circle with centre O. Chords AB, BC and CD are equal. If ∠DEF = 110o, calculate: (i) ∠AFE, (ii) ∠FAB.
Solution: Join \[AE,\text{ }OB\text{ }and\text{ }OC\] (i) As \[AOD\]is the diameter \[\angle AED\text{ }=\text{ }{{90}^{o}}~\] [Angle in a semi-circle is a right angle] But, given \[\angle DEF\text{...
In a cyclic-trapezium, the non-parallel sides are equal and the diagonals are also equal. Prove it.
Solution: Let \[ABCD\]be the cyclic trapezium in which \[AB\text{ }||\text{ }DC,\text{ }AC\text{ }and\text{ }BD\]are the diagonals. Required to prove: \[\left( i \right)\text{ }AD\text{ }=\text{...
From a window A, 10 m above the ground the angle of elevation of the top C of a tower is xo, where tan xo = 5/2 and the angle of depression of the foot D of the tower is yo, where tan yo = 1/4. Calculate the height CD of the tower in metres.
SOLUTION: Since, \[AB\text{ }=\text{ }DE\text{ }=\text{ }10\text{ }m\] So, in ∆ABC \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} DE/AE\text{ }=\text{ }tan\text{ }y\text{ }=\text{ }{\scriptscriptstyle 1\!/\!{ }_4} \\...
The angles of elevation of the top of a tower from two points on the ground at distances a and b meters from the base of the tower and in the same line are complementary. Prove that the height of the tower is √ab meter.
SOLUTION: Let AB to be the tower of height h meters and let C and D be two points on the level ground such that BC = b meters, BD = a meters, ∠ACB = α, ∠ADB = β. Given, \[\alpha \text{ }+\text{...
With reference to the given figure, a man stands on the ground at point A, which is on the same horizontal plane as B, the foot of the vertical pole BC. The height of the pole is 10 m. The man’s eye s 2 m above the ground. He observes the angle of elevation of C, the top of the pole, as xo, where tan xo = 2/5. Calculate: (i) the distance AB in metres; (ii) angle of elevation of the top of the pole when he is standing 15 metres from the pole. Give your answer to the nearest degree.
Let AD to be the height of the man, AD = 2 m. \[=>\text{ }CE\text{ }=\text{ }\left( 10\text{ }-\text{ }2 \right)\text{ }=\text{ }8\text{ }m\] (i) In ∆CED, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} CE/DE\text{...
A vertical tower stands on a horizontal plane and is surmounted by a vertical flagstaff of height h meter. At a point on the plane, the angle of elevation of the bottom of the flagstaff is α and at the top of the flagstaff is β. Prove that the height of the tower is h tan α/ (tan β – tan α).
SOLUTION: Let AB be the tower of height x metre, surmounted by a vertical flagstaff AD. Let C be a point on the plane such that ∠ACB = α, ∠ACB = β and AD = h. In ∆ABC, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}...
At a point on level ground, the angle of elevation of a vertical tower is found to be such that its tangent is 5/12. On walking 192 meters towards the tower, the tangent of the angle is found to be 3/4. Find the height of the tower.
SOLUTION: Let AB to be the vertical tower and C and D be the two points such that CD = 192 m. And let ∠ACB = θ and ∠ADB = α \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} tan\text{ }\theta \text{ }=\text{ }5/12 \\...
The radius of a circle is given as 15 cm and chord AB subtends an angle of 131o at the centre C of the circle. Using trigonometry, calculate: (i) the length of AB; (ii) the distance of AB from the centre C.
Since, CA = CB = 15 cm and ∠ACB = 131o Constructing a perpendicular CP from centre C to the chord AB,we get CP bisects ∠ACB as well as chord AB. =>∠ACP = 65.5o In ∆ACP, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}...
Calculate AB.
SOLUTION: In ∆AMOB, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} cos\text{ }{{30}^{o}}~=\text{ }AO/MO \\ \surd 3/2\text{ }=\text{ }AO/6 \\ AO\text{ }=\text{ }5.20\text{ }m \\ \end{array}\] In ∆BNO,...
Calculate BC.
SOLUTION: In ∆ADC, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} CD/AD\text{ }=\text{ }tan\text{ }{{42}^{o}} \\ CD\text{ }=\text{ }20\text{ x }0.9004\text{ }=\text{ }18.008\text{ }m \\ \end{array}\] In ∆ADB,...
In the following diagram, AB is a floor-board; PQRS is a cubical box with each edge = 1 m and ∠B = 60o. Calculate the length of the board AB.
SOLUTION: In ∆PSB, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} PS/PB\text{ }=\text{ }sin\text{ }{{60}^{o}} \\ PB\text{ }=\text{ }2/\text{ }\surd 3\text{ }=\text{ }1.155\text{ }m \\ \end{array}\] In ∆APQ,...
Find AD in FIG-1 and FIG-2
(i) FIG-1 SOLUTION: In ∆AEB, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} AE/BE\text{ }=\text{ }tan\text{ }{{32}^{o}} \\ AE\text{ }=\text{ }20\text{ x }0.6249\text{ }=\text{ }12.50\text{ }m \\ AD\text{ }=\text{...
The angle of elevation of the top of a tower is observed to be 60o. At a point, 30 m vertically above the first point of observation, the elevation is found to be 45o. Find: (i) the height of the tower, (ii) its horizontal distance from the points of observation.
Let AB to be the tower of height h meters and let the two points be C and D be such that CD = 30 m, ∠ADE = 45o and ∠ACB = 60o (i) In ∆ADE, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} AE/DE\text{ }=\text{ }tan\text{...
From the figure, given below, calculate the length of CD.
SOLUTION: In ∆AED, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} AE/\text{ }DE\text{ }=\text{ }tan\text{ }{{22}^{o}} \\ AE\text{ }=\text{ }DE\text{ }tan\text{ }{{22}^{o}}~=\text{ }15\text{ }x\text{ }0.404\text{...
Two pillars of equal heights stand on either side of a roadway, which is 150 m wide. At a point in the roadway between the pillars the elevations of the tops of the pillars are 60o and 30o; find the height of the pillars and the position of the point.
Let AB and CD be the two towers of height h m each and let P be a point in the roadway BD such that BD = 150 m, ∠APB = 60o and ∠CPD = 30o In ∆ABP, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} AB/BP\text{ }=\text{...
From the top of a light house 100 m high, the angles of depression of two ships are observed as 48o and 36o respectively. Find the distance between the two ships (in the nearest metre) if: (i) the ships are on the same side of the light house. (ii) the ships are on the opposite sides of the light house.
Let AB to be the lighthouse and the two ships be C and D such that ∠ADB = 36o and ∠ACB = 48o In ∆ABC, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} AB/BC\text{ }=\text{ }tan\text{ }{{48}^{o}} \\ BC\text{ }=\text{...
Find the height of a building, when it is found that on walking towards it 40 m in a horizontal line through its base the angular elevation of its top changes from 30o to 45o.
Let AB to be the building of height h meters. and let the two points be C and D be such that CD = 40 m, ∠ADB = 30o and ∠ACB = 45o In ∆ABC, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} AB/BC\text{ }=\text{ }tan\text{...
Find the height of a tree when it is found that on walking away from it 20 m, in a horizontal line through its base, the elevation of its top changes from 60 to 30.
Let AB to be the height of the tree, h m. and let the two points be C and D be such that CD = 20 m, ∠ADB = 30o and ∠ACB = 60o In ∆ABC, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} AB/BC\text{ }=\text{ }tan\text{...
In the figure, given below, it is given that AB is perpendicular to BD and is of length X metres. DC = 30 m, ∠ADB = 30 and ∠ACB = 45. Without using tables, find X.
In ∆ABC, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} AB/BC\text{ }=\text{ }tan\text{ }{{45}^{o}}~=\text{ }1 \\ =>\text{ }BC\text{ }=\text{ }AB\text{ }=\text{ }X \\ \end{array}\] In ∆ABD,...
A boy, 1.6 m tall, is 20 m away from a tower and observes the angle of elevation of the top of the tower to be (i) 45, (ii) 60. Find the height of the tower in each case.
Let the height of the tower to be ‘h’ m. (i) Since, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} \theta \text{ }=\text{ }{{45}^{o}} \\ tan\text{ }{{45}^{o}}~=\text{ }\left( h\text{ }-\text{ }1.6 \right)/\text{ }20 ...
A kite is attached to a string. Find the length of the string, when the height of the kite is 60 m and the string makes an angle 30o with the ground.
Let the length of the rope to be x meters. \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} sin\text{ }{{30}^{o}}~=\text{ }60/x \\ {\scriptscriptstyle 1\!/\!{ }_2}\text{ }=\text{ }60/x \\ x\text{ }=\text{ }120\text{ }m ...
Two persons are standing on the opposite sides of a tower. They observe the angles of elevation of the top of the tower to be 30o and 38o respectively. Find the distance between them, if the height of the tower is 50 m.
Let one of the persons be A , at a distance of ‘x’ meters and the second person be B at a distance of ‘y’ meters from the foot of the tower. The angle of elevation of A is 30o...
A ladder is placed along a wall such that its upper end is resting against a vertical wall. The foot of the ladder is 2.4 m from the wall and the ladder is making an angle of 68o with the ground. Find the height, up to which the ladder reaches.
Let the height upto which the ladder reaches as ‘h’ meters. the angle of elevation is 68o \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} =>\text{ }tan\text{ }{{68}^{o}}~=\text{ }h/\text{ }2.4 \\ 2.475\text{ }=\text{...
The angle of elevation of the top of a tower from a point on the ground and at a distance of 160 m from its foot, is found to be 60o. Find the height of the tower.
Let the height of the tower to be h meters. the angle of elevation is 60o => \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} tan\text{ }{{60}^{o}}~=\text{ }h/160 \\ \surd 3\text{ }=\text{ }h/160 \\ h\text{ }=\text{...
The height of a tree is √3 times the length of its shadow. Find the angle of elevation of the sun.
Let the length of the shadow of the tree to be x meters. Therefore, the height of the tree = √3 x meters If θ is the angle of elevation of the sun, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} =>\text{ }tan\text{...
If m and n are roots of the equation: 1/x – 1/(x-2) = 3: where x ≠ 0 and x ≠ 2; find m x n.
According to ques, \[~1/x\text{ }-\text{ }1/\left( x-2 \right)\text{ }=\text{ }3\] \[\left( x\text{ }-\text{ }2\text{ }\text{ }x \right)/\text{ }\left( x\left( x\text{ }-\text{ }2 \right)...
Find the solution of the quadratic equation 2×2 – mx – 25n = 0; if m + 5 = 0 and n – 1 = 0.
According to ques, \[m\text{ }+\text{ }5\text{ }=\text{ }0\text{ }and\text{ }n\text{ }\text{ }1\text{ }=\text{ }0\] hence, \[m\text{ }=\text{ }-5\text{ }and\text{ }n\text{ }=\text{ }1\] putting...
If p – 15 = 0 and 2×2 + px + 25 = 0: find the values of x.
According to the given question, \[p\text{ }\text{ }15\text{ }=\text{ }0\] And \[2{{x}^{2}}~+\text{ }px\text{ }+\text{ }25\text{ }=\text{ }0\] Thus, \[p\text{ }=\text{ }15\] Using\[p\]in the...
Show that one root of the quadratic equation x2 + (3 – 2a)x – 6a = 0 is -3. Hence, find its other root.
According to the given equation, \[{{x}^{2}}~+\text{ }\left( 3\text{ }\text{ }2a \right)x\text{ }\text{ }6a\text{ }=\text{ }0\] By putting \[x\text{ }=\text{ }-3\]we get \[{{\left( -3...
One root of the quadratic equation 8×2 + mx + 15 = 0 is ¾. Find the value of m. Also, find the other root of the equation.
According to the given question, \[8{{x}^{2~}}+\text{ }mx\text{ }+\text{ }15\text{ }=\text{ }0\] One of the roots is\[~{\scriptscriptstyle 3\!/\!{ }_4},\]and it satisfies the given equation So,...
Solve: 2x – 3 = √(2×2 – 2x + 21)
According to the given question, \[2x\text{ }\text{ }3\text{ }=\text{ }\surd (2{{x}^{2}}~\text{ }2x\text{ }+\text{ }21)\] Squaring on both sides, we get \[{{\left( 2x\text{ }\text{ }3...
Solve: . ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\text{ }\mathbf{3}\surd \mathbf{2}{{\mathbf{x}}^{\mathbf{2}}}~\text{ }\mathbf{5x}\text{ }\text{ }\surd \mathbf{2}\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{0}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-22ead8085663c05474ddb007572bafdc_l3.png)
According to the given question, \[3\surd 2{{x}^{2}}~\text{ }5x\text{ }\text{ }\surd 2\text{ }=\text{ }0\] Or, \[3\surd 2{{x}^{2}}~\text{ }6x\text{ }+\text{ }x\text{ }\text{ }\surd 2\text{ }=\text{...
solve: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\text{ }\mathbf{3}{{\mathbf{x}}^{\mathbf{2}}}~\text{ }\mathbf{2}\surd \mathbf{6x}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{2}\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{0}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d5146bd91c51cf5cda3cc06dbd2ed9d1_l3.png)
According to the given equation, \[3{{x}^{2}}~\text{ }2\surd 6x\text{ }+\text{ }2\text{ }=\text{ }0\] Or, \[3{{x}^{2}}~\text{ }\surd 6x\text{ }\text{ }\surd 6x\text{ }+\text{ }2\text{ }=\text{ }0\]...
Solve: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\text{ }\left( \mathbf{x}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{5} \right)\text{ }\left( \mathbf{x}\text{ }\text{ }\mathbf{5} \right)\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{24}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-85409799f13ae2131936b8199e40aef0_l3.png)
According to the given question, \[\left( x\text{ }+\text{ }5 \right)\text{ }\left( x\text{ }\text{ }5 \right)\text{ }=\text{ }24\] Or, \[{{x}^{2}}~\text{ }25\text{ }=\text{ }24\] Or,...
Solve: (x^2+1/x^2)-3(x-1/x)-2=0
Let \[\left( x\text{ }\text{ }1/x \right)\text{ }=\text{ }y\text{ }\ldots .\text{ }\left( 1 \right)\] squaring on both sides \[{{\left( x\text{ }\text{ }1/x \right)}^{2}}~=\text{ }{{y}^{2}}\] or,...
Solve: 2(x^2+1/x^2)-(x+1/x)=11
let \[\left( x\text{ }+\text{ }1/x \right)\text{ }=\text{ }y\text{ }\ldots .\text{ }\left( 1 \right)\] squaring on both sides \[{{\left( x\text{ }+\text{ }1/x \right)}^{2}}~=\text{ }{{y}^{2}}\]...
Solve:9(x^2+1/x^2)-9(x+1/x)-52=0
Let, \[~\left( x\text{ }+\text{ }1/x \right)\text{ }=\text{ }y\text{ }\ldots .\text{ }\left( 1 \right)\] squaring both sides \[{{\left( x\text{ }+\text{ }1/x \right)}^{2}}~=\text{ }{{y}^{2}}\]...
Solve: x4 – 2×2 – 3 = 0
According to ques, \[{{x}^{4}}~\text{ }2{{x}^{2}}~\text{ }3\text{ }=\text{ }0\] Let’s take \[{{x}^{2}}~=\text{ }y\] Then, the equation becomes \[{{y}^{2}}~\text{ }2y\text{ }\text{ }3\text{ }=\text{...
Find the value of x, given that A^2 = B,
Solution: So, on comparison we get \[x\text{ }=\text{ }36.\]
If given matrix, find the matrix X such that: A + X = 2B + C
Solution: As per the given question,
Solve : 2×4 – 5×2 + 3 = 0
According to ques, \[~2{{x}^{4}}~\text{ }5{{x}^{2}}~+\text{ }3\text{ }=\text{ }0\] Let \[{{x}^{2}}~=\text{ }y\] The, \[2{{y}^{2}}~\text{ }5y\text{ }+\text{ }3\text{ }=\text{ }0\] \[2{{y}^{2}}~\text{...
If given matrix, find the matrix ‘X’ and matrix ‘Y’.
Solution: Now, On comparison, we get \[-28\text{ }-\text{ }3x\text{ }=\text{ }10\] \[3x\text{ }=\text{ }-38\] \[x\text{ }=\text{ }-38/3\] And, \[20\text{ }-\text{ }3y\text{ }=\text{ }-8\] \[3y\text{...
Find x and y, if:
Solution: According to the given question, On comparison, we get \[2x\text{ }+\text{ }3x\text{ }=\text{ }5\] And \[2y\text{ }+\text{ }4y\text{ }=\text{ }12\] \[5x\text{ }=\text{ }5\text{ }and\text{...
Solve: x + 4/x = -4; x ≠ 0
According to ques, \[~x\text{ }+\text{ }4/x\text{ }=\text{ }-4\] or, \[\left( {{x}^{2~}}+\text{ }4 \right)/\text{ }x\text{ }=\text{ }-4\] Or, \[{{x}^{2}}~+\text{ }4\text{ }=\text{ }-4x\] or,...
Solve: (i) A (BA) (ii) (AB) B.
Solution: \[\left( i \right)\text{ }A\text{ }\left( BA \right)\] \[\left( ii \right)\text{ }\left( AB \right)\text{ }B\]
Find the values of a, b and c.
Solution: According to the given ques, On comparison, we get \[a\text{ }+\text{ }1\text{ }=\text{ }5\Rightarrow a\text{ }=\text{ }4\] \[b\text{ }+\text{ }2\text{ }=\text{ }0\Rightarrow b\text{...
Solve: x2 – 11/4 x + 15/8 = 0
According to ques, \[~{{x}^{2}}~\text{ }11/4\text{ }x\text{ }+\text{ }15/8\text{ }=\text{ }0\] Taking L.C.M , \[\left( 8{{x}^{2}}~\text{ }22x\text{ }+\text{ }15 \right)/\text{ }8\text{ }=\text{ }0\]...
3A x M = 2B; find matrix M.
Solution: According to the given question, \[3A\text{ }x\text{ }M\text{ }=\text{ }2B\] Suppose the order of the \[matrix\text{ }M\text{ }be\text{ }\left( a\text{ }x\text{ }b \right)\] Now, we know...
Solve : a2x2 – b2 = 0
According to ques, \[{{a}^{2}}{{x}^{2}}~\text{ }{{b}^{2}}~=\text{ }0\] or, \[{{\left( ax \right)}^{2}}~\text{ }{{b}^{2}}~=\text{ }0\] Or, \[\left( ax\text{ }+\text{ }b \right)\left( ax\text{ }\text{...
Evaluate:
Solution: As per the given question,
Solve: (i) The order of the matrix X. (ii) The matrix X.
Solution: (i) Suppose, the order of the matrix be \[a\text{ }x\text{ }b\] We know that Hence, for product of matrices to be possible \[a\text{ }=\text{ }2\] And, form the order of the resultant...
Solve: (2x + 3)2 = 81
According to ques, \[{{\left( 2x\text{ }+\text{ }3 \right)}^{2}}~=\text{ }81\] Taking square root both sides, \[2x\text{ }+\text{ }3\text{ }=\text{ }\pm \text{ }9\] Or, \[2x\text{ }=\text{ }\pm...
If given matrix , find x and y, if: (i) x, y ∈ W (whole numbers) (ii) x, y ∈ Z (integers)
Solution: According to the given question, \[{{x}^{2}}~+\text{ }{{y}^{2}}~=\text{ }25\] And, \[-2{{x}^{2}}~+\text{ }{{y}^{2}}~=\text{ }-2\] \[\left( i \right)\text{ }x,\text{ }y~\in ~W\text{ }\left(...
Find x and y, if:
Solution: On comparison, we get \[3x\text{ }+\text{ }18\text{ }=\text{ }15\] And \[12x\text{ }+\text{ }77\text{ }=\text{ }10y\] \[3x\text{ }=\text{ }-3\] And \[y\text{ }=\text{ }\left( 12x\text{...
Solve each of the following equations: 2x/x-3+1/2x+3+3x+9/(x-3)(2x+3)=0; x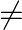 3,x
3,x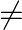 -3/2
-3/2
According to ques, \[4{{x}^{2}}~+\text{ }6x\text{ }+\text{ }x\text{ }\text{ }3\text{ }+\text{ }3x\text{ }+\text{ }9\text{ }=\text{ }0\] Or, \[4{{x}^{2}}~+\text{ }10x\text{ }+\text{ }6\text{ }=\text{...
Find x and y, if:
Solution: On comparison, we get \[6x\text{ }-\text{ }10\text{ }=\text{ }8\] And \[-2x\text{ }+\text{ }14\text{ }=\text{ }4y\] \[6x\text{ }=\text{ }18\] And \[y\text{ }=\text{ }\left( 14\text{...
If the given matrix. simplify: A2 + BC.
Solution: \[{{A}^{2}}~+\text{ }BC\]
If given matrix. Then show that: (i) A(B + C) = AB + AC (ii) (B – A)C = BC – AC.
Solution: \[\left( i \right)\text{ }A\left( B\text{ }+\text{ }C \right)\] \[AB\text{ }+\text{ }AC\] So, \[A\left( B\text{ }+\text{ }C \right)\text{ }=\text{ }AB\text{ }+\text{ }AC\] \[\left( ii...
If given matrix and A2 = I, find a and b.
Solution: \[{{A}^{2}}\] Given, \[~{{A}^{2~}}=\text{ }I\] On comparison, we get \[1\text{ }+\text{ }a\text{ }=\text{ }1\] \[a\text{ }=\text{ }0\] And, \[-1\text{ }+\text{ }b\text{ }=\text{ }0\]...
The sum of the ages of a father and his son is 45 years. Five years ago, the product of their ages (in years) was 124. Determine their present ages.
let the present ages of father and his son be \[~x\text{ }years\text{ }and\text{ }\left( 45\text{ }\text{ }x \right)\text{ }years\] hence five years ago, Father’s age \[=\text{ }\left( x\text{...
Find the matrix A, if B =given matrix and B2 = B + ½A.
Solution: \[{{B}^{2}}\] \[{{B}^{2}}~=\text{ }B\text{ }+\text{ }{\scriptscriptstyle 1\!/\!{ }_2}A\] \[{\scriptscriptstyle 1\!/\!{ }_2}A\text{ }=\text{ }{{B}^{2}}-\text{ }B\] \[A\text{ }=\text{...
Solve : (i) (A + B)^2 (ii) A2 + B2
Solution: According to the given ques, \[\left( i \right)\text{ }\left( A\text{ }+\text{ }B \right)\] \[So,\text{ }{{\left( A\text{ }+\text{ }B \right)}^{2}}~=\text{ }\left( A\text{ }+\text{ }B...
The sum S of first n even natural numbers is given by the relation S = n(n + 1). Find n, if the sum is 420.
According to ques, \[S\text{ }=\text{ }n\left( n\text{ }+\text{ }1 \right)\] Also, \[S\text{ }=\text{ }420\] So, \[n\left( n\text{ }+\text{ }1 \right)\text{ }=\text{ }420\] Or, \[{{n}^{2}}~+\text{...
Solve: (i) AB (ii) A^2 – AB + 2B
Solution: \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\text{ }\mathbf{AB}\text{ }\] \[\left( ii \right)\text{ }{{\mathbf{A}}^{\mathbf{2}}}-\text{ }\mathbf{AB}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{2B}\]
Two trains leave a railway station at the same time. The first train travels due west and the second train due north. The first train travels 5 km/hr faster than the second train. If after 2 hours, they are 50 km apart, find the speed of each train.
Let the speed of the second train be \[~x\text{ }km/hr.\] Then, the speed of the first train is \[\left( x\text{ }+\text{ }5 \right)\text{ }km/hr\] Let O be the position of the railway station,...
Solve: (i) A – B (ii) A^2
Solution: \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\text{ }\mathbf{A}\text{ }-\text{ }\mathbf{B}\text{ }\] \[\text{ }\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\text{ }{{\mathbf{A}}^{\mathbf{2}~}}\]
BA = M^2, find the values of a and b.
Solution: $BA$ \[{{M}^{2}}\] So, \[BA\text{ }={{M}^{2}}\] On comparison, we get \[-2b\text{ }=\text{ }-2\] \[b\text{ }=\text{ }1\] And, \[a\text{ }=\text{ }2\]
If the given matrix and I is a unit matrix of the same order as that of M; show that: M2 = 2M + 3I
Solution: \[{{M}^{2}}\] \[2M\text{ }+\text{ }3I\] Hence, \[{{M}^{2}}~=\text{ }2M\text{ }+\text{ }3I\]
A plane left 30 minutes later than the schedule time and in order to reach its destination 1500 km away in time, it has to increase its speed by 250 km/hr from its usual speed. Find its usual speed.
Let the usual speed of the plane to be \[x\text{ }km/hr\] The distance to travel \[=\text{ }1500km\] since, Time = Distance/ Speed As the ques suggests, \[{{x}^{2}}~+\text{ }250x\text{ }\text{...
Find A2 + AC – 5B
Solution: \[{{A}^{2}}\] $AC$ $5B$ \[{{A}^{2}}~+\text{ }AC\text{ }-\text{ }5B\text{ }=\]
Is the following possible: A^2
Solution: \[{{A}^{2}}~=\text{ }A\text{ }x\text{ }A,\text{ }\]isn’t possible because the number of columns isn’t equal to its number of rows in matrix A.
Rs 6500 was divided equally among a certain number of persons. Had there been 15 persons more, each would have got Rs 30 less. Find the original number of persons.
let the original number of persons to be x. According to ques, Total money which was divided is \[=\text{ }Rs\text{ }6500\] Each person’s share is \[=\text{ }Rs\text{ }6500/x\] Then, as the question...
Is the following possible: (i) AB (ii) BA
Solution: \[\left( i \right)\text{ }AB\] \[\left( ii \right)\text{ }BA\]
Solve: (i) (AB) C (ii) A (BC)
Solution: According to the given ques, \[\left( i \right)\text{ }\left( AB \right)\] \[\left( AB \right)\text{ }C\] \[\left( ii \right)\text{ }BC\] \[A\text{ }\left( BC \right)\] So, \[\text{...
An aeroplane travelled a distance of 400 km at an average speed of x km/hr. On the return journey, the speed was increased by 40 km/hr. Write down an expression for the time taken for: (i) the onward journey; (ii) the return journey. If the return journey took 30 minutes less than the onward journey, write down an equation in x and find its value.
According to ques, Distance \[=\text{ }400\text{ }km\] Average speed of the airplane \[=\text{ }x\text{ }km/hr\] Also, speed while returning \[=\text{ }\left( x\text{ }+\text{ }40 \right)\text{...
Find x and y, if:
Solution: (i) On comparison, we get \[5x\text{ }-\text{ }2\text{ }=\text{ }8\] \[5x\text{ }=\text{ }10\] \[x\text{ }=\text{ }2\] And, \[20\text{ }+\text{ }3x\text{ }=\text{ }y\] \[20\text{ }+\text{...
A hotel bill for a number of people for overnight stay is Rs 4800. If there were 4 people more, the bill each person had to pay, would have reduced by Rs 200. Find the number of people staying overnight.
Let the number of people staying overnight as x. According to ques, total hotel bill \[~=\text{ }Rs\text{ }4800\] Now,hotel bill for each person \[=\text{ }Rs\text{ }4800/x\] therefore,...
If find x and y when x and y when A2 = B.
Solution: \[{{A}^{2}}~\] \[{{A}^{2}}~=\text{ }B\] On comparison, we get \[4x\text{ }=\text{ }16\] \[x\text{ }=\text{ }4\] And, \[1\text{ }=\text{ }-y\] \[y\text{ }=\text{ }-1\]
If the given matrix and I is a unit matrix of order 2×2, find: (i) A^2 (ii) B^2A
Solution: (i) \[{{A}^{2}}\] (ii) \[~{{B}^{2}}\] \[{{B}^{2}}A\]
A trader buys x articles for a total cost of Rs 600. (i) Write down the cost of one article in terms of x. If the cost per article were Rs 5 more, the number of articles that can be bought for Rs 600 would be four less. (ii) Write down the equation in x for the above situation and solve it for x.
According to ques, Number of articles \[=\text{ }x\] And, the total cost of articles \[=\text{ }Rs\text{ }600\] Again, (i) Cost of one article \[=\text{ }Rs\text{ }600/x\] (ii) also,...
If the given matrix and I is a unit matrix of order 2×2, find: (i) AI (ii) IB
Solution: (i) AI = (ii) IB=
If given matrix and I is a unit matrix of order 2×2, find: (i) AB (ii) BA
Solution: According to the given question (i) (ii)
The distance by road between two towns A and B is 216 km, and by rail it is 208 km. A car travels at a speed of x km/hr and the train travels at a speed which is 16 km/hr faster than the car. Calculate: (iii) If the train takes 2 hours less than the car, to reach town B, obtain an equation in x and solve it. (iv) Hence, find the speed of the train.
(iii) According to the question, \[4x\text{ }+\text{ }1728\text{ }=\text{ }{{x}^{2}}~+\text{ }16x\] Or, \[{{x}^{2}}~+\text{ }12x\text{ }\text{ }1728\text{ }=\text{ }0\] Or, \[{{x}^{2}}~+\text{...
Evaluate: if possible: If not possible, give reason.
Solution: The product of the given matrices isn’t possible as per the rule the number of columns in the first matrix isn’t equal to the number of rows in the second matrix.
Evaluate: if possible: If not possible, give reason.
Solution: \[=\text{ }\left[ 6\text{ }+\text{ }0 \right]\text{ }=\text{ }\left[ 6 \right]\] \[=\text{ }\left[ -2+2\text{ }3-8 \right]\text{ }=\text{ }\left[ 0\text{ }-5 \right]\]
The distance by road between two towns A and B is 216 km, and by rail it is 208 km. A car travels at a speed of x km/hr and the train travels at a speed which is 16 km/hr faster than the car. Calculate: (i) the time taken by the car to reach town B from A, in terms of x; (ii) the time taken by the train to reach town B from A, in terms of x.
According to ques, Speed of car = \[x\text{ }km/hr\] Speed of train = \[\left( x\text{ }+\text{ }16 \right)\text{ }km/hr\] Time = \[Distance/\text{ }Speed\] (i)Time taken by the car to reach town B...
(i) find the matrix 2A + B. (ii) find a matrix C such that:
(ii) Solution: (i) \[2A\text{ }+\text{ }B\] (ii)
Solve:
Solution: According to the given question, the matrix is
From given data below find (i) 2A – 3B + C (ii) A + 2C – B
Solution: \[\left( i \right)\text{ }2A\text{ }-\text{ }3B\text{ }+\text{ }C\] \[\left( ii \right)\text{ }A\text{ }+\text{ }2C\text{ }-\text{ }B\]
Find x and y if: (i) 3[4 x] + 2[y -3] = [10 0]
(ii) Solution: From L.H.S, we have \[3\left[ 4\text{ }x \right]\text{ }+\text{ }2\left[ y\text{ }-3 \right]\] \[=\text{ }\left[ 12\text{ }3x \right]\text{ }+\text{ }\left[ 2y\text{ }-6 \right]~\]...
Evaluate:
(I) (ii) Solution: According to the given ques, (i) (ii)
Evaluate: (i) 3[5 -2]
(ii) Solution: (i) \[3\left[ 5\text{ }-2 \right]\text{ }=\text{ }\left[ 3\times 5\text{ }3x-2 \right]\text{ }=\text{ }\left[ 15\text{ }-6 \right]\] (ii)
In a G.P., the ratio between the sum of first three terms and that of the first six terms is 125: 152. Find its common ratio.
According to the given ques, Hence, the common ratio is \[3/5.\]
How many terms of the series 2 + 6 + 18 + ….. must be taken to make the sum equal to 728?
. According to the given question, G.P: \[2\text{ }+\text{ }6\text{ }+\text{ }18\text{ }+\text{ }\ldots ..\] Here, \[a\text{ }=\text{ }2\] And \[r\text{ }=\text{ }6/2\text{ }=\text{ }3\] Also given,...
Find the sum of G.P.: 3, 6, 12, …., 1536.
According to the given question, G.P: \[3,\text{ }6,\text{ }12,\text{ }\ldots .,\text{ }1536\] So, \[a\text{ }=\text{ }3,\text{ }l\text{ }=\text{ }1536\] and \[r\text{ }=\text{ }6/3\text{ }=\text{...
A geometric progression has common ratio = 3 and last term = 486. If the sum of its terms is 728; find its first term.
According to the given question, For a G.P., \[r\text{ }=\text{ }3,\text{ }l\text{ }=\text{ }486\] and \[{{S}_{n}}~=\text{ }728\] \[1458\text{ }-\text{ }a\text{ }=\text{ }728\text{ }x\text{ }2\text{...
The 4th term and the 7th term of a G.P. are 1/27 and 1/729 respectively. Find the sum of n terms of the G.P.
According to the given question, \[{{t}_{4}}~=\text{ }1/27\] and \[{{t}_{7~}}=\text{ }1/729\] We know that, \[{{t}_{n}}~=\text{ }a{{r}^{n\text{ }-\text{ }1}}\] So, \[{{t}_{4~}}=\text{...
A boy spends Rs.10 on first day, Rs.20 on second day, Rs.40 on third day and so on. Find how much, in all, will he spend in 12 days?
Amount spent on \[{{1}^{st}}~day\text{ }=\text{ }Rs\text{ }10\] Amount spent on \[{{2}^{nd}}~day\text{ }=\text{ }Rs\text{ }20\] Amount spent on \[{{3}^{rd}}~day\text{ }=\text{ }Rs\text{ }40\]...
The first term of a G.P. is 27 and its 8th term is 1/81. Find the sum of its first 10 terms.
\[First\text{ }term\text{ }\left( a \right)\text{ }of\text{ }a\text{ }G.P\text{ }=\text{ }27\] And, \[{{8}^{th}}~term\text{ }=\text{ }{{t}_{8}}~=\text{ }a{{r}^{8\text{ }-\text{ }1}}~=\text{ }1/81\]...
How many terms of the geometric progression 1 + 4 + 16 + 64 + …….. must be added to get sum equal to 5461?
According to the given question, G.P: \[1\text{ }+\text{ }4\text{ }+\text{ }16\text{ }+\text{ }64\text{ }+\text{ }\ldots \ldots ..\] Here, \[a\text{ }=\text{ }1\text{ }and\text{ }r\text{ }=\text{...
Find the sum of G.P.:
(i) (ii) Solution: (i) According to the given question Here, \[a\text{ }=\text{ }\left( x\text{ }+\text{ }y \right)/\text{ }\left( x\text{ }-\text{ }y \right)\] And \[~r\text{ }=\text{ }1/\left[...
Find the sum of G.P.: (i) 1 – 1/2 + 1/4 – 1/8 + …….. to 9 terms (ii) 1 – 1/3 + 1/32 – 1/33 + ……… to n terms
(i) According to the given question G.P: \[1\text{ }-\text{ }1/2\text{ }+\text{ }1/4\text{ }-\text{ }1/8\text{ }+\text{ }\ldots \ldots ..\text{ }to\text{ }9\text{ }terms\] Here, \[a\text{ }=\text{...
Find the sum of G.P.: (i) 1 + 3 + 9 + 27 + ………. to 12 terms (ii) 0.3 + 0.03 + 0.003 + 0.0003 +….. to 8 terms.
(i) According to the given question G.P: \[1\text{ }+\text{ }3\text{ }+\text{ }9\text{ }+\text{ }27\text{ }+\text{ }\ldots \ldots \ldots .\text{ }to\text{ }12\text{ }terms\] Here, \[a\text{ }=\text{...
If for a G.P., pth, qth and rth terms are a, b and c respectively; prove that: (q – r) log a + (r – p) log b + (p – q) log c = 0
The first term of the G.P. be A and its common ratio be R. Hence, \[{{p}^{th}}~term\text{ }=\text{ }a\text{ }\Rightarrow \text{ }A{{R}^{p\text{ }-\text{ }1}}~=\text{ }a\] \[{{q}^{th}}~term\text{...
Find the G.P. 1/27, 1/9, 1/3, ……, 81; find the product of fourth term from the beginning and the fourth term from the end.
According to the given question, G.P. \[1/27,\text{ }1/9,\text{ }1/3,\text{ }\ldots \ldots ,\text{ }81\] Here, \[a\text{ }=\text{ }1/27,\] \[common\text{ }ratio\text{ }\left( r \right)\text{...
Find the third term from the end of the G.P. 2/27, 2/9, 2/3, ……., 162
Given series: \[2/27,\text{ }2/9,\text{ }2/3,\text{ }\ldots \ldots .,\text{ }162\] Here, \[a\text{ }=\text{ }2/27\] \[r\text{ }=\text{ }\left( 2/9 \right)\text{ }/\text{ }\left( 2/27 \right)\]...
Prove that : (v) 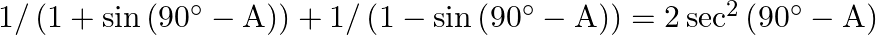
Prove that : (iii) 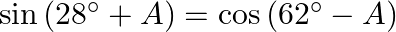 (iv)
(iv) 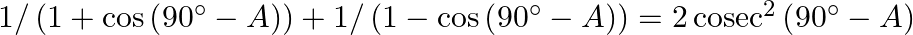
(iii) $\sin \left(28^{\circ}+\mathrm{A}\right)=\sin \left[90^{\circ}-\left(62^{\circ}-\mathrm{A}\right)\right]=\cos \left(62^{\circ}-\mathrm{A}\right)$ (iv)
Find the seventh term from the end of the series: √2, 2, 2√2, …… , 32
Given series: \[\surd 2,\text{ }2,\text{ }2\surd 2,\text{ }\ldots \ldots \text{ },\text{ }32\] Here, \[a\text{ }=\text{ }\surd 2\] \[r\text{ }=\text{ }2/\text{ }\surd 2\text{ }=\text{ }\surd 2\]...
Prove that: (i) 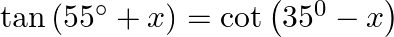 (ii)
(ii) 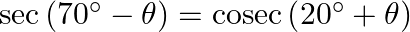
(i) $\tan \left(55^{\circ}+x\right)=\tan \left[90^{\circ}-\left(35^{\circ}-x\right)\right]=\cot \left(35^{\circ}-x\right)$ (ii) $\sec \left(70^{\circ}-\theta\right)=\sec...
Evaluate: (vii) 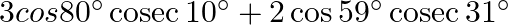 (viii)
(viii) 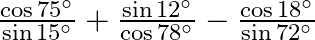
(vii) $3 \cos 80^{\circ} \operatorname{cosec} 10^{\circ}+2 \cos 59^{\circ} \operatorname{cosec} 31^{\circ}$ $=3 \cos (90-10)^{0} \operatorname{cosec} 10^{\circ}+2 \cos (90-31)^{0}...
The product of 3rd and 8th terms of a G.P. is 243. If its 4th term is 3, find its 7th term
According to the given question, Product of \[{{3}^{rd}}~and\text{ }{{8}^{th}}\] terms of a G.P. is \[243\] The general term of a G.P. First term \[a\] And Common ratio \[r\]is given by,...
Evaluate : (v) 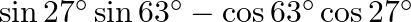 (vi)
(vi) 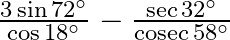
(v) $\sin 27^{\circ} \sin 63^{\circ}-\cos 63^{\circ} \cos 27^{\circ}$ $=\sin (90-63)^{0} \sin 63^{\circ}-\cos 63^{\circ} \cos (90-63)^{\circ}$ $=\cos 63^{\circ} \sin 63^{\circ}-\cos 63^{\circ} \sin...
Evaluate : (iii) 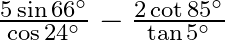 (iv)
(iv) 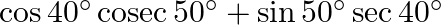
(iii) (iv) $\cos 40^{\circ} \operatorname{cosec} 50^{\circ}+\sin 50^{\circ}$ sec $40^{\circ}$ $=\cos (90-50)^{0} \operatorname{cosec} 50^{\circ}+\sin (90-50)^{0} \sec 40^{\circ}$ $=\sin 50^{\circ}...
Evaluate:(i) 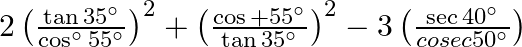 (ii)
(ii) 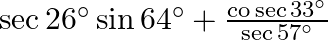
(i) (ii) 1+1=2
If the first and the third terms of a G.P are 2 and 8 respectively, find its second term.
According to the given question, \[{{t}_{1}}~=\text{ }2\text{ }and\text{ }{{t}_{3}}~=\text{ }8\] General term is \[{{t}_{n}}~=\text{ }a{{r}^{n\text{ }-\text{ }1}}\] So, \[{{t}_{1}}~=\text{...
Fourth and seventh terms of a G.P. are 1/18 and -1/486 respectively. Find the G.P.
Given, \[{{t}_{4}}~=\text{ }1/18\text{ }and\text{ }{{t}_{7}}~=\text{ }-1/486\] General term is \[{{t}_{n}}~=\text{ }a{{r}^{n\text{ }-\text{ }1}}\] So, \[{{t}_{4}}~=\text{ }a{{r}^{4\text{ }-\text{...
The fifth term of a G.P. is 81 and its second term is 24. Find the geometric progression.
According to the given question, \[{{t}_{5}}~=\text{ }81\text{ }and\text{ }{{t}_{2}}~=\text{ }24\] We know that, General term is \[{{t}_{n}}~=\text{ }a{{r}^{n\text{ }-\text{ }1}}\] So,...
(i) If 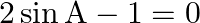 , show that:
, show that: 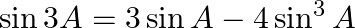 (ii) If
(ii) If 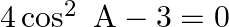 , show that:
, show that: 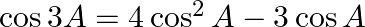
(i) Since, $2 \sin \mathrm{A}-1=0$ Therefore, $\sin A=1 / 2$ since, $\sin 30^{\circ}=1 / 2$ Hence, $\mathrm{A}=30^{\circ}$ LHS = $\sin 3 A=\sin 3\left(30^{\circ}\right)=\sin 30^{\circ}=1$...
If tan A = n tan B and sin A = m sin B, prove that: cos^2 A = m^2 – 1/ n^2 – 1
$\tan A=n \tan B$ $n=\tan A / \tan B$ And, $\sin A=m \sin B$ $\mathrm{m}=\sin \mathrm{A} / \sin \mathrm{B}$ Substituting RHS in $\mathrm{m}$ and $\mathrm{n}$ $m^{2}-1 / n^{2}-1$...
If 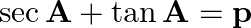 , show that:
, show that: 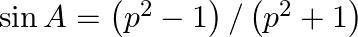
RHS, $\left(p^{2}-1\right) /\left(p^{2}+1\right)$ $=\frac{(\sec A+\tan A)^{2}-1}{(\sec A+\tan A)^{2}+1}$ $=\frac{\sec ^{2} A+\tan ^{2} A+2 \tan A \sec A-1}{\sec ^{2} A+\tan ^{2} A+2 \tan A \sec...
If 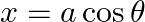 and
and 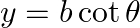 , show that:
, show that: 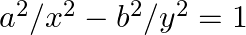
LHS = $a^{2} / x^{2}-b^{2} / y^{2}$ $=\frac{a^{2}}{a^{2} \cos ^{2} \theta}-\frac{b^{2}}{b^{2} \cot ^{2} \theta}$ $=\frac{1}{\cos ^{2} \theta}-\frac{\sin ^{2} \theta}{\cos ^{2} \theta}$...
If sin A + cos A = p and sec A + cosec A = q, then prove that: q(p^2 – 1) = 2p
LHS = $q\left(p^{2}-1\right)=(\sec A+\operatorname{cosec} A)\left[(\sin A+\cos A)^{2}-1\right]$ $=(\sec A+\operatorname{cosec} A)\left[\sin ^{2} A+\cos ^{2} A+2 \sin A \cos A-1\right]$ $=(\sec...
Which term of the G.P. :
Solution: In the given G.P. First term, \[a\text{ }=\text{ }-10\] Common ratio, \[r\text{ }=\text{ }\left( 5/\surd 3 \right)/\text{ }\left( -10 \right)\text{ }=\text{ }1/\left( -2\surd 3 \right)\]...
Prove: (xv) 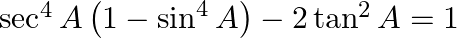 (xvi)
(xvi) 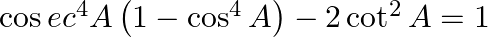
(xv) LHS = $\sec ^{4} \mathrm{~A}\left(1-\sin ^{4} \mathrm{~A}\right)-2 \tan ^{2} \mathrm{~A}$ $=\sec ^{4} \mathrm{~A}\left(1-\sin ^{2} \mathrm{~A}\right)\left(1+\sin ^{2} \mathrm{~A}\right)-2 \tan...
Prove : (xvii) 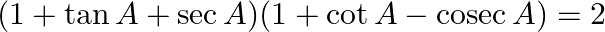
$(1+\tan A+\sec A)(1+\cot A-\operatorname{cosec} A)$ $=1+\cot A-\operatorname{cosec} A+\tan A+1-\sec A+\sec A+\operatorname{cosec} A-\operatorname{cosec} A \sec A$ $=2+\cos \mathrm{A} / \sin...
Prove : (xiii) 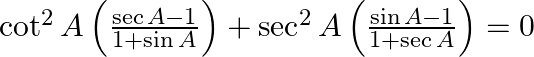 (xiv)
(xiv) 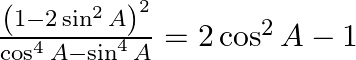
LHS = = RHS (xiv) LHS = = RHS
The mid-point of the line segment joining (2a, 4) and (-2, 2b) is (1, 2a + 1). Find the value of a and b.
According to the given question, The mid-point of \[\left( 2a,\text{ }4 \right)\text{ }and\text{ }\left( -2,\text{ }2b \right)\text{ }is\text{ }\left( 1,\text{ }2a\text{ }+\text{ }1 \right)\] By...
Prove : (xi) 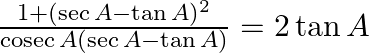 (xii)
(xii) 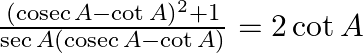
LHS = = RHS (xii) LHS = = RHS
Prove (ix) 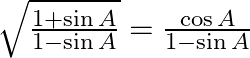 (x)
(x) 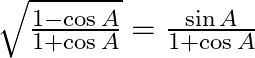
LHS= = RHS (x) LHS =
Prove : (vii) 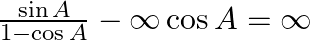 (viii)
(viii) 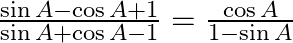
(vii) LHS =$=(\sin A /(1-\cos A))-\cot A$ Since, $\cot A=\cos A / \sin A$ $=\left(\sin ^{2} A-\cos A+\cos ^{2} A\right) /(1-\cos A) \sin A$ $=(1-\cos A) /(1-\cos A) \sin A$ $=1 / \sin \mathrm{A}$...
Prove: (v) 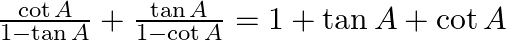 (vi)
(vi) 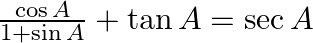
(v) LHS= cot A/ (1 – tan A) + tan A/ (1 – cot A) = RHS (vi) LHS= cos A/ (1 + sin A) + tan A = RHS
The mid-point of the line-segment joining (4a, 2b – 3) and (-4, 3b) is (2, -2a). Find the values of a and b.
According to the given question, The mid-point of the line-segment joining \[\left( 4a,\text{ }2b\text{ }-\text{ }3 \right)\text{ }and\text{ }\left( -4,\text{ }3b \right)\text{ }is\text{ }\left(...
Prove: (iii) 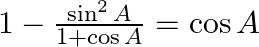 (iv)
(iv) 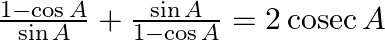
(iii) LHS= 1 – sin2 A/ (1 + cos A) = RHS (iv) LHS= (1 – cos A)/ sin A + sin A/ (1 – cos A) = RHS
Find the co-ordinates of the centroid of a triangle ABC whose vertices are: A (-1, 3), B (1, -1) and C (5, 1)
By the centroid of a triangle formula, we get the co- ordinates of the centroid of triangle \[ABC\]as \[=\text{ }\left( 5/3,\text{ }1 \right)\]
Use tables to find sine of: (i) 21° (ii) 34° 42′
(i) Taking LHS, $1 /(\cos A+\sin A)+1 /(\cos A-\sin A)$ (ii) Taking LHS, $\operatorname{cosec} A-\cot A$ $=\frac{1}{\sin A}-\frac{\cos A}{\sin A}$ $=\frac{1-\cos A}{\sin A}$ $=\frac{1-\cos A}{\sin...
AB is a diameter of a circle with centre C = (-2, 5). If A = (3, -7), find (i) the length of radius AC (ii) the coordinates of B.
(i) \[Radius\text{ }AC\text{ }=\text{ }\surd [\text{ }{{\left( 3\text{ }+\text{ }2 \right)}^{2}}~+\text{ }{{\left( -7\text{ }-\text{ }5 \right)}^{2}}~]\] \[=\text{ }\surd [\text{ }({{5}^{2}}~+\text{...
Use trigonometrical tables to find tangent of: (iii) 17° 27′
(iii) $\tan 17^{\circ} 27^{\prime}=\tan \left(17^{\circ} 24^{\prime}+3^{\prime}\right)=0.3134+0.0010=0.3144$
