In the sample space, there are 216 outcomes, with each element of the sample space having three entries and taking the form ![]() where
where ![]() .
.
Considering the event, E: 4 appears on the third toss
Now the event, F: 6 and 5 appears respectively on the first two tosses
We get the common sample space of both,
![]()
So, ![]()
Now, we know that by definition of conditional probability, 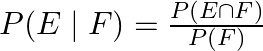
Now by substituting the values we get
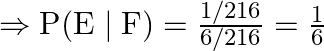
![]()
